The story of construction tools – a journey through time
As societies advanced and civilizations flourished, so too did the tools they used to construct their buildings. A gradual move from simple stone tools to bronze and iron marked significant technological breakthroughs, enabling builders to create more complex and durable structures. The Industrial Revolution brought about a further transformation, with the introduction of powerful machinery and innovative materials.
Today, the construction industry stands at the forefront of technological advancement. Cutting-edge tools and techniques are revolutionising the way we build, from 3D printing and drones to advanced materials and sustainable practices. As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the evolution of construction tools remains a testament to human ingenuity and our unwavering commitment to progress - and this is their story.
In the early years, construction was a monumental undertaking, relying on simple yet effective tools crafted from stone. Hammers, chisels and wedges were the primarily used to quarry stone, shape timber and erect structures. These rudimentary tools, forged from the earth itself, were the foundation upon which the earliest civilizations were built.
The ingenuity of our ancestors is evident in the remarkable structures they erected using these basic tools. The pyramids of Egypt, stand as testaments to the skill and dedication of the ancient Egyptians. Stonehenge, another iconic structure, showcases the precision and complexity that could be achieved with stone tools.
The process of construction in the Stone Age was laborious and time-consuming. Quarrying stone required immense physical exertion, as workers used hammers and chisels to break away large blocks from the bedrock. Timber was felled using stone axes and shaped with simple hand tools. The transportation of heavy materials was a significant challenge, often requiring teams of workers to haul stones and logs to the construction site.
Despite the limitations of their tools, Stone Age builders demonstrated remarkable ingenuity and skill. They developed techniques for lifting and moving heavy stones, constructing intricate structures, and aligning buildings with celestial bodies. These early achievements laid the foundation for the development of more advanced construction techniques and tools in subsequent eras.
The Stone Age tools used in construction were not only functional but also often adorned with intricate carvings and designs. These decorations reflect the cultural and spiritual beliefs of the people who created them. The tools themselves were not merely instruments of labour but also objects of pride and craftsmanship.
The legacy of the Stone Age builders can be seen in the many ancient structures that still stand today. These monuments are not only testaments to human ingenuity but also provide valuable insights into the lives and cultures of our ancestors. The simple tools used to create these structures remind us of the remarkable achievements of our early ancestors and the enduring power of human ingenuity.
The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age, a period which saw the widespread use of bronze tools, marked a significant advancement in human civilization. The discovery of metallurgy, the process of extracting and working with metals, revolutionised the construction industry. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, was a stronger and more durable material than stone, allowing for the creation of more sophisticated and efficient tools.
Bronze tools, such as axes and saws and adzes were essential for building projects during this era. Axes were used to cut timber for construction, while saws allowed for more precise cuts. Adzes, with their curved blades, were used to shape stone and wood. These tools were more durable and efficient than their stone predecessors, enabling builders to construct larger and more complex structures.
The Bronze Age also saw a shift toward more focused construction techniques. The use of bronze tools allowed for greater precision and accuracy in shaping materials, leading to more intricate and ornate structures. Bronze was further used to create decorative elements, such as metalwork and sculptures, that adorned buildings and temples.
The development of bronze tools also had a profound impact on trade and commerce. Bronze was a valuable resource, and the ability to produce bronze objects enabled civilizations to engage in trade and exchange with other cultures. This increased interaction led to the diffusion of knowledge and technology, fostering cultural exchange and innovation.
The Iron Age
The Iron Age, was marked by the widespread use of iron tools, marked another significant milestone in the evolution of construction. Iron, a stronger and more versatile material than bronze, marked another change for the industry, enabling builders to construct larger and more complex structures.
Iron tools, such as hammers, chisels and nails, were more durable and efficient than their bronze predecessors. These tools allowed for greater precision and accuracy in construction, enabling builders to create intricate details and complex designs.
The availability of iron also facilitated the development of new construction techniques. Iron nails, for example, were essential for securing wooden structures together, allowing for larger and more stable buildings. Iron tools were also used to shape stone and metal, creating decorative elements and structural components.
The increased strength and durability of iron tools enabled builders to construct larger and more complex structures, such as bridges, aqueducts and fortifications. These monumental works of engineering showcased the technological advancements of the Iron Age.
The Iron Age also saw the development of different construction tools, such as the trowel and the level. These tools allowed for more precise and efficient construction work, leading to higher-quality structures.
The impact of iron tools extended beyond construction. The ability to produce iron led to advancements in other industries, such as agriculture and warfare. The Iron Age was a period of significant technological and cultural development and the construction industry played a vital role in shaping this era.
The legacy of the Iron Age can be seen in the many ancient structures that still stand today. These structures, built with iron tools, are testaments to the ingenuity and skill of our ancestors. The Iron Age marked a turning point in the history of construction, paving the way for future advancements and innovations.
The Middle Ages
The Middle Ages, a period spanning from the fall of the Roman Empire to the Renaissance, witnessed significant advancements in construction tools and techniques. The development of tools, such as the trowel, the level and the plumb rule, allowed for more precise and efficient construction work.
The trowel, a hand tool used for applying and smoothing mortar, became an indispensable tool for bricklayers and masons. The level, a measuring instrument used to ensure surfaces are horizontal or vertical, was crucial for achieving accurate and stable structures. The plumb rule, a weighted tool used to determine verticality, was essential for ensuring the alignment of walls and columns.
These particular tools, combined with the knowledge and skills of skilled craftsmen, enabled builders to create more intricate and complex structures. Cathedrals, castles and other monumental buildings were constructed during this period, showcasing the advancements in construction techniques.
The invention of the wheel and pulley also changed construction during the Middle Ages. These simple but effective machines made it possible to move heavy materials and equipment more easily, reducing the physical labour required for construction projects. The wheelbarrow, a combination of the wheel and the barrow, became a common sight on construction sites, facilitating the transportation of materials.
The Middle Ages also saw the development of new construction materials, such as stained glass and Gothic architecture. Stained glass windows, with their intricate designs and vibrant colours, adorned cathedrals and other religious buildings. Gothic architecture, illustrated by its soaring arches and pointed vaults, pushed the boundaries of structural engineering and aesthetic beauty.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid technological and economic growth, further transformed the construction industry. The development of steam power and machinery led to the invention of new tools that dramatically increased the efficiency and productivity of construction projects.
Steam-powered cranes, for example, altered the ability to lift and move heavy materials. These machines replaced the need for manual labour, allowing for faster and more efficient construction. Excavators, powered by steam and later by internal combustion engines, made it possible to excavate large amounts of earth and rock quickly and efficiently.
Other significant advancements in construction tools during the Industrial Revolution included the invention of electric and pneumatic power tools, such as drills, saws and grinders, which made construction work more efficient and less physically demanding.
The development of concrete mixers allowed for the rapid and efficient production of concrete, together with a wide range of other machines, such as bulldozers, designed to meet the needs of large-scale construction projects.
The Industrial Revolution also led to the development of new construction materials, such as steel and reinforced concrete. These materials, combined with advanced construction techniques, enabled the construction of larger, taller and more complex structures.
The 20th century witnessed further advancements in construction technology. The development of concrete and steel as structural materials revolutionised building techniques. Power tools, such as drills, saws, and grinders, became essential for construction workers. The invention of heavy machinery, such as bulldozers, excavators, and cranes, made it possible to move large amounts of earth and materials efficiently.
In recent decades, technological advancements have continued to shape the construction industry. Computer-aided design (CAD) software has changed the design and planning of construction projects. Building information modelling (BIM) has become an essential tool for visualising and managing complex projects.
Automation and robotics are also playing an increasingly important role in construction. Robotic systems can be used for tasks such as bricklaying, welding, and painting. Drones are used for surveying and monitoring construction sites, while 3D printing is being explored for creating custom components and structures.
The evolution of construction tools has been a driving force behind human progress. From the simple stone tools of our ancestors to the sophisticated technology of today, these tools have enabled us to build remarkable structures that have shaped our world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative tools and techniques emerging in the construction industry.
Additional Articles

Why modern builders still use tools invented thousands of years ago
Walk onto a modern construction site and you will see plenty of laser levels, drones, tablets and power tools. Yet look a little closer and something unexpected becomes clear. Alongside all this...
Read moreThe elevator that changed the world when Elisha Otis cut the rope
Today, stepping into a lift is one of the most routine acts of modern life. We press a button, glance at the floor indicator, and trust, almost without thinking. that a metal box will safely carry us...
Read more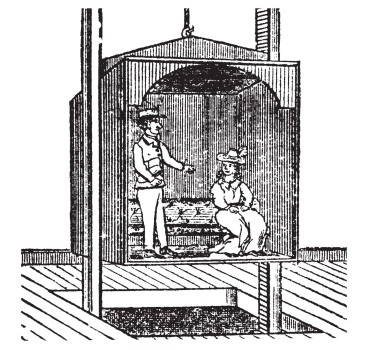

How the Romans invented central heating
Central heating feels like a modern convenience, yet its core principles were mastered nearly two thousand years ago. Long before boilers, radiators and underfloor heating systems, the Romans...
Read more